
Elements Of Marine Insurance
Organisation of Qualifications & Awards
The main aim of this unit is to provide learners a clear knowledge and understanding of the principles of marine and general transport insurance markets and to familiarise them with the organisations involved in maritime insurance operations
Upon successful completion of the course students will be able to:
Learning and teaching methods/strategies used to enable the achievement of learning outcomes:
Learning takes place on a number of levels through lectures, class discussion including problem review and analysis. Formal lectures provide a foundation of information on which the student builds through directed learning and self managed learning outside of the class. The students are actively encouraged to form study groups to discuss course material which fosters a greater depth learning experience.
Relevant experience is taken into consideration for students 21 years of age and over who have not completed any formal qualifications.
Nature of Policies:
Main types
Partial Loss Total Loss – Active Constructive
Relevant factors:
York Antwerp Rules, 1974
General Average (relevant factors)
Reeds Marine Insurance, B. Jervis (MacMillan)
Marine Insurance Principles and Practice F.Templeman (Qureshi Press)
Marine Insurance Law O.Gurses (Routledge)
Tutorial support includes feedback on assignments and may vary by college according to local needs and wishes.
Advance reading and preparation / Class preparation / Background reading / Group study / Portfolio / Diary etc
Working through the course text and completing assignments as required will take up the bulk of the learning time. In addition students are expected to engage with the tutor and other students and to undertake further reading using the web and/or libraries.
Final Examination: 70%
Coursework: 30%
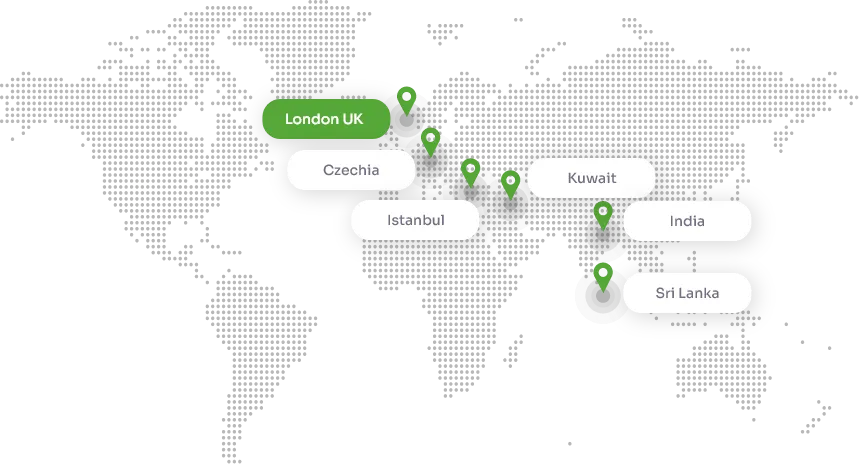
OQA has approved study centres worldwide. Select the your country to see available centres in that area.
3rd Floor, 2-4 Commercial Street, London E1 6LP
2-4, Commercial Street, 3rd Floor London, England, E1 6LP
Hamilton House, 4 Mabledon Pl London WC1H 9BB
160 Jhumat House, London Road IG11 8BB
Its FREE and can be unsubscribed anytime